Thin-film thermoforming
Thermoforming definition :
This process consists to transform thermoplastic materials such as films, sheet and plates to 3D object. Thermoplastic materials take a rubbery consistency in high temperature.
At this time, the plastic is easily form by a tooling and frozen in this form by cooling.
Choosing your thermoforming method depends on :
- Deformation to be imposed
- The shape of manufacturing object
- Type of thermoforming material
- Material thickness
- Economics means : machines, molds, number of series …
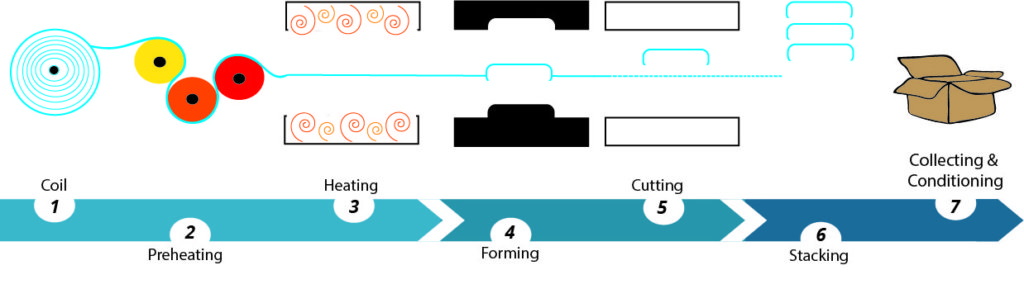
Thin-film thermoforming :
We using the term thin thickness when the plastic is a bobine. The thin-film thermoforming consists in taking this plastic coil, heating it to soften it, applying it to a mold to convert the plastic by suction.
Thin-film thermoforming advantages :
- Cadences more important
- Shorter heating time
- Various applications
- Reactivity
Type of product :
- Shell
- Trays
- Pots
- Blisters
- Shipping trays
- Casting mold
- Boxes
- Coffrets
Benefits of plastic material in packaging :
- Lightness: their density is between 0.92 and 1.39 and can go down to 0.01 for expanded materials.
- Mechanical resistance: variable according to the polymers, it can reach high values as for polycarbonate.
- Transparency: many plastics are transparent or translucent
- Inalterability: plastics are resistant to external aggressions (humidity, microorganism …)
- Aesthetics: the infinite variety of shape, their beautiful appearance and their colors make it possible to make packaging of the most attractive.
- Waterproofing: Even under a thin layer, plastics are a serious obstacle to moisture and gases. The use of so-called complex composite materials reinforces this function.
- Natural asepsis: during processing, plastic materials are heated to temperatures between 110 ° C and 190 ° C. This temperature brings asepsis to the packaging they constitute.